|
Dynamic Local
Analysis Abstract:
¡°Dynamic Local Analysis¡± is an algorithm to establish mathematic model with
the big data. On the basis of its features to search for the local samples
closest to the specimen and to establish models with local samples, the
problem of low confidence level of big data modeling is solved, and the model
calculation accuracy is increased. 1. Preface With the development of information
technology, long-time data acquisition of the process of things results in
the increasing of dimensions, the largening of scope, the rising of density,
and more complex changes of the stored data which is called the big data
accordingly. Provided that the data is two-dimensional and is put into a
rectangular coordinate system (as shown in Fig. 1), it is obvious that to
find a mathematic model as an accurate fit is of great difficulty. To solve
this problem, we develop the method called "Dynamic Local Analysis¡±.
Fig.
1 2. Dynamic Local Analysis 2.1
The stored big data are compared through illustration to distinguish
outliners and the compliance of regular patterns. The unreasonable samples
are eliminated, and the screened samples are used to establish a standard
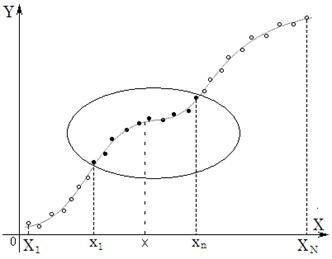
sample group(x1£¬y1£¬x2£¬y2 £¬¡¡ xi£¬yi £¬¡¡ xm£¬ym, m is the sample size, as all data points shown in Fig. 2. 2.2. When the specimen is to calculate y
via x, the x value is to be compared with xi in the standard sample group
in sequence to find out m sets of local samples (x1£¬y1£¬x2£¬y2 £¬¡¡ xi£¬yi £¬¡¡ xn£¬yn) , which are the closest to
the specimen, n is set according to actual conditions, as solid core data
points shown in Fig. 2; n sets of local samples are used to establish model
to calculate the y value. 2.3. The hollow points out of the circle in
Fig. 2 are remote from the specimen and have very little influence which can
be ignored from the calculation.
Fig. 2 3. Conclusion 3.1. When y is calculated with the
different specimen, the data to establish model is different; as a result,
the models change dynamically. 3.2. The samples used for modeling are part
of all samples, so it is thus local. 3.3. The local samples used for regression
modeling are simpler in curve variation compared to the whole of samples;
therefore, the confidence level of modeling is increased and the accuracy of
calculated results is improved. |