
Principle

Least Square Method
◆ The "least square method" is a mathematical method to find the mathematical relationship of relevant data. It is widely used in data processing in many disciplines.
◆ in 1801, Gauss invented the "least square method" and calculated the orbit of Ceres. French scientist Legendre also invented the "least square method" in 1806.

New Square Method
◆ The "New square method" is an improved approach based on the “least square method”. It calculates not only the constants and coefficients but also the variables’ power values in a model in the course of data regression calculations, thus bringing about a simpler and more accurate calculation for non-linear data regression processes.
◆ The "New square method" is a nonlinear regression method we developed due to the deficiency of our directed towards "least square method".

Method Comparison
◆ The "least square method" is a special case of the "new square method". The "new square method" calculates the power value (any real number) k of the dependent variable. The "least square method" defaults the power value k of the dependent variable to 1
◆ The "new square method" uses the calculation of power value to make the regression model function curve bend with different curvature to better fit the data with different curvature and better fit the regression model with the data.
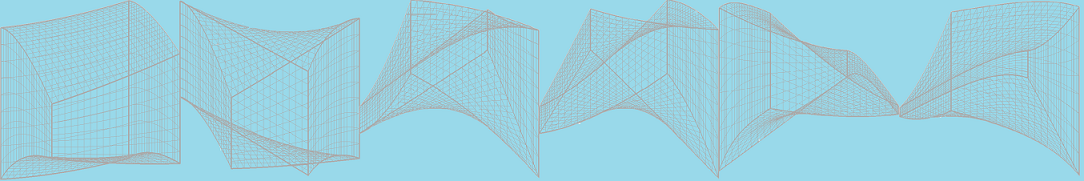
Demonstration







COMMUNICATE
BDA
Language: Simplified Chinese
Size: 37.9 MB
Description:Big data analysis system
(BDA) is a collection version of
quality control chart (QCC), data
regression analysis (DRS) and system
process analysis(SPA).
 COMMUNICATE
COMMUNICATE
QCC
Language: Simplified Chinese
Size: 27.3 MB
Description:Quality control chart
(QCC) is a quality control tool
prepared according to the
national standard of the people's
Republic of China "GB_T_4091-2001".
 COMMUNICATE
COMMUNICATE
DRS
Language: Simplified Chinese
Size: 34.1 MB
Description:Data regression analysis
(DRS) was prepared according to
"New Square Method". It makes the
regression calculation of one-
dimensional and multi-dimensional
linear and nonlinear data simpler
and the result more accurate.
 COMMUNICATE
COMMUNICATE
SPA
Language: Simplified Chinese
Size: 36.8 MB
Description:System process analysis
(SPA) is a tool to analyze the data
of various relationships within a
system, establish mathematical
relationships and calculate. It
is widely used in practice.
 COMMUNICATE
COMMUNICATE
 Email: ww_yypp@163.com
Email: ww_yypp@163.com
 Wechat number: eaihua8
Wechat number: eaihua8